Think once “Why not to reduce our footprint to plastic’s use?”
Plastics have a significant impact on various ecosystem services and climate change. Plastics do not biodegrade quickly and can persist in our environment for decades, releasing toxic chemicals. Microplastics can harm soil health and decrease soil fertility, which ultimately affects the plant’s growth leads to impacts in crop production. The accumulation of plastics in natural habitats can disrupt the ecology of the ecosystem by altering the natural food chain. Plastic wastes are also the
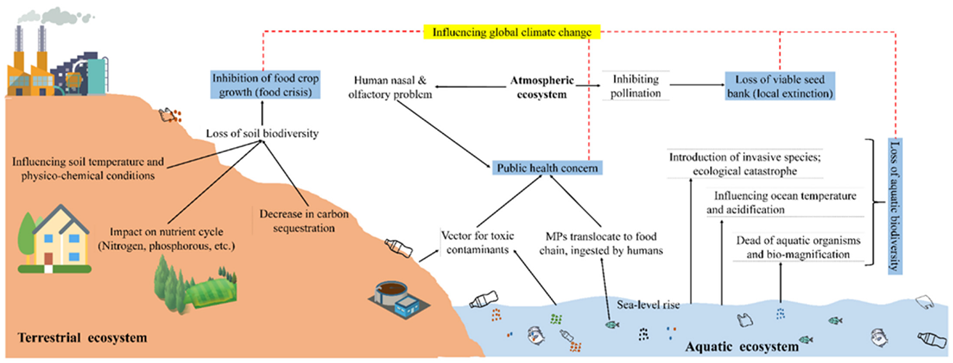
Fig: Illustration of plastics affecting various ecosystem services and climate change on terrestrial, aquatic, and atmospheric ecosystems (Pic source: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179963)
major sources of water pollution like when it break down into smaller particles, known as microplastics, they can contaminate water bodies, leading to the ingestion of plastics by aquatic animals and bioaccumulation in the food chain. The marine pollution, causing significant harm to marine ecosystem; entangle and kill the marine animals, block sunlight from reaching to aquatic plants and microorganisms and by releasing the toxic chemicals that can cause illness or death. Besides, the impacts on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, it also impacts on atmospheric ecosystems through GHGs emissions and toxic chemicals release into the air during the process of production, transportation and disposal which exacerbate the climate change and global warming and harming the human health.
Hence, the impacts of plastics on ecosystem services and climate change are significant and far-reaching. Reducing plastic use, improving waste management practices, and promoting sustainable alternatives to plastics are critical to mitigating these impacts.
- By Ms. Amrita Pokharel (Climate Change Expert at PEEDA)